What Does The Future Of Cold Chain Shipping Look Like?
By Chevy Beh | First published: July 20, 2020 Updated: September 15, 2021
Post COVID-19, logistics and cold-chain technologies are essential for the future of healthcare.
When a healthcare crisis hits, cold chain logistics races to the top of the global agenda. We’ve seen it all in the last 18 months: vaccine research; clinical trials; equipping medical centers with the drugs they need; global vaccine roll-out and ongoing research. For global recovery to continue, our COVID-19 experience has proven one thing: the healthcare supply chain is crucial to all citizens, not just the sick. So where is the industry headed?
We’ll start at the beginning.
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines cold chain as an end-to-end system of storing and transporting vaccines or healthcare products at desired temperatures from the point of manufacture to the point of use. The need for temperature-specific solutions is critical for biopharma, vaccines and clinical trials. Unsurprisingly, demand for cold chain materials is expected to increase.
Cold chain and COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic really is the black swan that forced many global healthcare companies to rethink and transform their global supply chain model. Many are changing the way they operate in order to stay relevant – and afloat.
As vaccine roll-outs continue, the need for temperature-controlled shipments has become a priority for governments, media, health insurance companies, and social care. Of course, it’s a priority for ordinary global citizens and frontline workers too. We all want normalcy to be restored. This is where healthcare logistics comes into play.
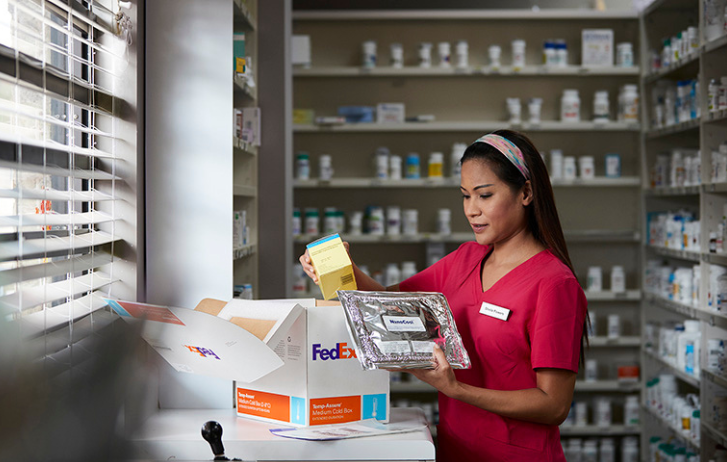
Healthcare supply chains require special conditions and standards that need to be met by trustworthy and experienced logistics providers, so pharmaceutical products reach patients in optimal condition. Some of these precise conditions include temperature control, humidity levels, and security.
COVID-19 continues to impact communities around the world, causing supply chain backlogs, shortages in medical aid deliveries and other medical related delays. That is why the successful delivery of life-saving medicines, especially in times of COVID-19, relies heavily on a reliable logistics provider who can continue to deliver even in the most disruptive of circumstances.
For example, my team and I developed BookDoc, which is an end-to-end digital healthcare platform to connect patients and medical practitioners across Asia Pacific. Although BookDoc was established before the pandemic, the virus has made us realize the importance of linking those in need of medical solutions to healthcare professionals remotely. Malaysia was a suitable launching pad for BookDoc in Southeast Asia because of the country’s solid telecommunication infrastructure, smart phone penetration, abundance of the middle class and strong rule of law.
Cold chain logistics plays a large role in a patient’s journey from detection and diagnosis to adherence, particularly regarding prescription medication which is often sent through cold chain. It is important that prescriptions sourced far from the patient’s location arrive in time and in perfect condition.
Evolution and increase in demand
The significance of cold chain logistics continues to evolve as the healthcare industry grows. According to Allied Market Research, one in two healthcare products is shipped via cold chain. There’s also been an increase in the demand for biopharmaceutical products at a higher rate than the demand for chemical drugs. And the surge in demand for vaccines has also propelled the total sales volume of temperature-controlled pharmaceutical products in Asia Pacific, which is double the rate of the pharmaceutical industry as a whole.
And of course, Asia Pacific’s ever-growing population is what drives the demands for medical support and cold chain shipping in the region. According to World Meters, the current population in Asia Pacific stands at 4.46 billion, with the world population at 7.8 billion. This implies that Asia Pacific accounts for over 56% of the global population, which heavily influences the region’s consumption of food and healthcare products and services.
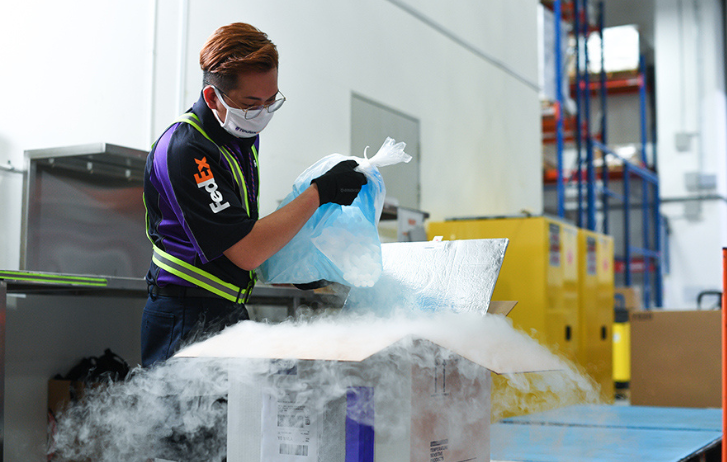
It’s not only about healthcare, either. Cold chain also applies to the freezing solutions required to maintain the quality and shelf life of products such as fresh agricultural produce, seafood, and frozen foods. Besides maintaining quality, cold chain is also essential for avoiding over capacity and reducing transport bottlenecks during peak periods. In many of the above cases, FedEx has been able to step in when smaller supply chain managers or logistics companies were unable to fulfill their usual quotas.
A reliable partner
With their robust global network and logistics experts who understand the nature of critical supply chains and cold chain needs, FedEx ensures that customers experience convenience and peace of mind when it comes to shipping.
Given the current climate, it is so critical that the cold chain logistics industry functions efficiently and reliably. With the help of logistics providers, the industry is expected to continue to evolve and grow. And anything that can aid the healthcare sector with rapid transportation and delivery of essential pharmaceuticals during these trying times is something to be thankful for.
For more information about shipping during COVID-19, head here.
SHARE THIS STORY
- How To Ship A Giant Panda
- How To Make Freight Shipments Work For Your Small Business
- The Rise Of Intra-Asia Trade: Opportunities In The China-Southeast Asia Corridor
- Southeast Asia: The Next Manufacturing Powerhouse?
- 8 Most Unusual Shipments In The History Of FedEx
- Where Do Old Planes Go When They Retire?
Sign up now and save on your shipping rates!
Sign up now and earn discounts by shipping instantly with FedEx Ship ManagerTM at fedex.com.
Recommended For You
Introducing The Latest Megatrends In E-Commerce
Digital megatrends are transforming logistics. We look ahead to map how these shifts in online and consumer behavior can benefit SMEs.
Read More
How To Build Resilient And Reliable Healthcare Supply Chains
Logistics sector leaders are set up to help healthcare providers smooth the pain points in supply chain management in an uncertain world.
Read More
5 Ways SMEs Can Future Proof Their Business
From a stronger e-commerce strategy to re-examining working from home, explore the biggest contributors for post-COVID business recovery for SMEs.
Read More


