FedEx history
Growing and evolving since 1973
We’re proud to be one of the most admired brands in the world and one of the
best places to work. Here’s a look at some of the milestones along our journey.
We’re proud to be one of the most admired brands in the world and one of the best places to work. Here’s a look at some of the milestones along our journey.
1965
Frederick W. Smith wrote a term paper at Yale University proposing a revolutionary way to accommodate time-sensitive shipments—and received an average grade.
1971
Mr. Smith founded Federal Express Corporation in Little Rock, Arkansas.
Federal Express: What's in a name?
Mr. Smith thought the word “federal” suggested an interest in nationwide economic activity, and hoped the name would resonate with the Federal Reserve Bank, a potential customer.
1973
April 17, 1973: Federal Express began operations in Memphis, Tennessee, with 389 team members. That night, 14 aircraft delivered 186 packages to 25 U.S. cities.
Why Memphis?
- It’s centrally located in the U.S.
- Its airport was rarely closed because of bad weather.
- The airport was willing to make improvements for the operation.
- Additional hangar space was readily available.
1975
Installed our first drop box.
1977
Bought seven Boeing 727s after two years of lobbying led to Congress deregulating air cargo.
1978
Federal Express listed on the New York Stock Exchange as FDX.
1981
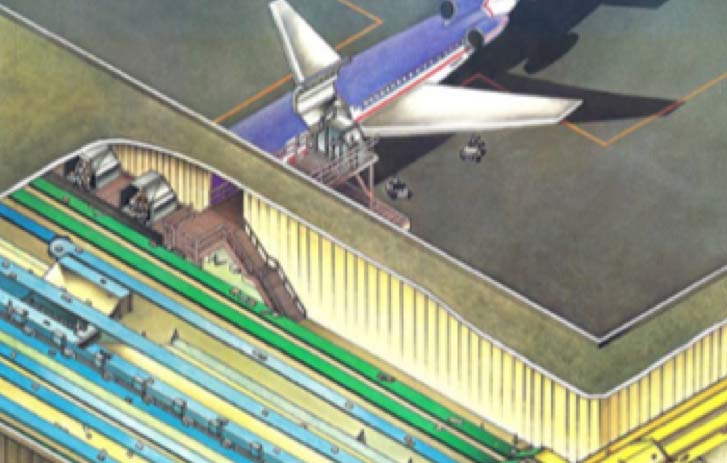
Introduced the overnight letter; began delivery to Canada; opened our super-hub next to Memphis International Airport.
1983
Made American business history as the first company to reach $1 billion in revenues within 10 years of startup without mergers or acquisitions.
1984
Started intercontinental operations with service to Europe and Asia.
1985
Roadway Package System (RPS), later Caliber System Inc., changed the direction of the small-package industry by using barcodes to track packages.
1986
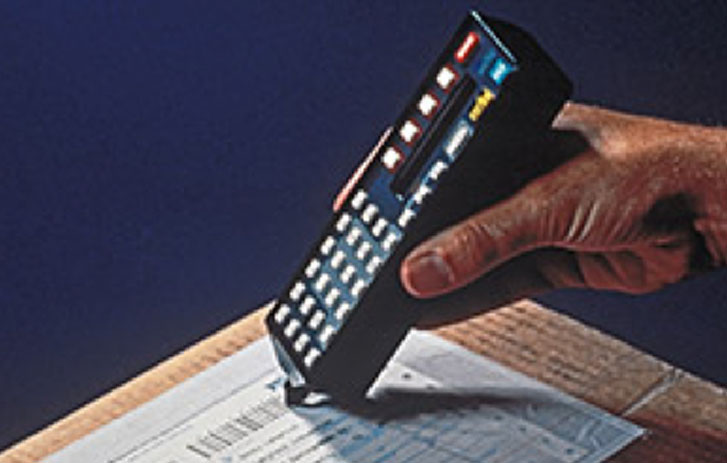
Introduced SuperTracker® hand-held barcode scanner.
1988
Started cargo service to Japan.
1989
Acquired Tiger International.
1990
Won the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award in the service category—the first company to do so.
1993
RPS exceeded $1 billion in annual revenue—the fastest growth of any ground transportation company in history.
1994
Rebranded as FedEx; launched fedex.com, the first transportation website with online package tracking.
1995
Became the only U.S.-based, all-cargo carrier with rights to serve China.
1996
RPS offered 100 percent coverage of North America.
1996
Introduced FedEx interNetShip®, now FedEx Ship Manager®, enabling customers to process shipments online for the first time.
1998
Acquired Caliber System and its subsidiaries.
2000
FDX renamed FedEx Corporation; introduced tech solutions including FedEx® Global Trade Manager and FedEx Ship Manager®.
2000
Renamed FedEx to FedEx Express, reflecting our position in the overall FedEx Corporation portfolio of services and further positioning us as an express carrier.
2000
Began operations, providing IT, sales, and marketing support for FedEx Express and FedEx Ground, and later for FedEx Freight and FedEx Office.
2000
Rebranded RPS as FedEx Ground following the acquisition of Caliber companies.
2000
Launched FedEx Home Delivery®.
2000
Formed FedEx Trade Networks with the acquisition of Tower Group International and World Tariff, Ltd.
2001
Created FedEx Freight by combining two acquisitions, Viking and American Freightways, to offer convenient shipping for LTL customers.
2002
Rebranded Tower Group International as FedEx Trade Networks Transport & Brokerage, Inc.
2002
Formed FedEx Trade Networks Trade Services, Inc., to incorporate duty and tax data services of WorldTariff with Trade & Customs Advisory Services.
2004
Acquired Parcel Direct, later rebranded FedEx Ground Economy.
2004
Acquired Kinko’s—operational since 1970—a provider of copying, printing, film processing, and office supplies to individuals, businesses, and commercial print buyers through its 800+ stores; rebranded it as FedEx Kinko’s Office and Print Services.
2004
Acquired Kinko’s, rebranded as FedEx Kinko’s, then as FedEx Office in 2008.
2005
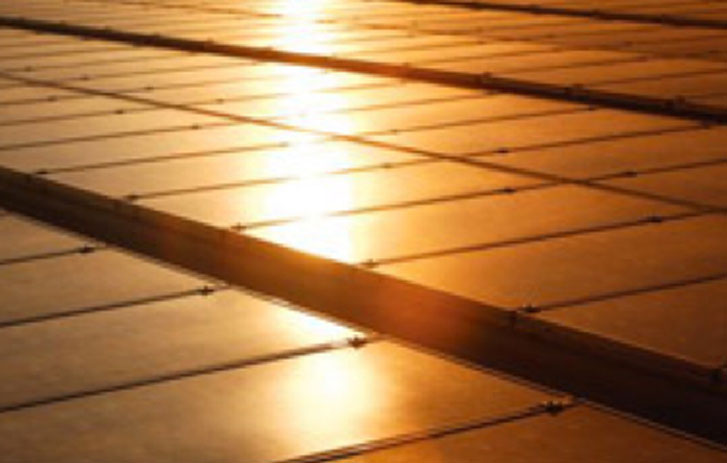
Started around-the-world flights; unveiled California’s largest corporate solar-power installation at our Oakland hub.
2006
Launched FedExCup® with the PGA TOUR.
2006
Rebranded Watkins acquisition as FedEx National LTL and FedEx Freight Canada.
2008
Introduced Boeing 757 freighters to our fleet for a new cargo service route between Memphis and Washington, D.C., demonstrating our commitment to reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
2008
Rebranded to FedEx Office.
2008
Kicked off aggressive expansion, opening offices around the globe, giving FedEx Trade Networks access to nearly all the world’s GDP through international air and ocean freight forwarding, customs brokerage, distribution and warehousing, and other services.
2009
Introduced SenseAware®, providing near real-time visibility and insight into shipment conditions mid-transit.
2010
Announced first all-electric trucks.
2011
Merged FedEx National LTL with FedEx Freight, launching its two service offerings, FedEx Freight® Priority and FedEx Freight® Economy, at all lengths of haul across the U.S. network.
2013
Launched FedEx Delivery Manager®.
2013
Added more fuel-efficient Boeing 767-300F planes to our fleet; launched 30+ initiatives to improve fuel efficiency and cut fuel emissions.
2013
Launched FedEx Delivery Manager® to allow U.S. customers to schedule dates, locations, and times of delivery, and track and manage deliveries en route.
2014
Acquired Bongo International and rebranded as FedEx Cross Border, providing duty and tax calculations, export compliance management, HS classification, currency conversions, shopping cart management, and protection against credit card fraud.
2015
Acquired GENCO, rebranded as FedEx Cross Border (North America).
2016
Acquired TNT Express (Europe).
2017
Opened $100 million International Express and Cargo Hub in Shanghai, China; delivered thousands of tons of medical supplies, food, and water to Texas, Florida, Puerto Rico, and other areas hit by natural disasters.
2017
Rebranded GENCO as FedEx Supply Chain.
2018
Realigned specialty logistics and e-commerce solutions under FedEx Trade Networks.
2019
Announced three transformational operational changes: year-round, seven-day residential delivery; the integration of FedEx Ground Economy volume into standard operations; and the addition of large-package capabilities.
2019
Introduced FedEx Freight Direct to meet growing e-commerce market needs for delivery of heavy, bulky products to or through the door for residences and businesses.
2019
Renamed FedEx Trade Networks to FedEx Logistics, providing air and ocean freight forwarding, supply chain solutions, customs brokerage, and trade management tools and data from a single, trusted source.
2020
FedEx Dataworks organization is established to apply the powerful data insights generated by the FedEx network to build digital solutions that create new opportunities for our customers, their customers, and for the FedEx of tomorrow.
2021
Unveiled Priority Earth: Our initiative to deliver a more sustainable future with a goal of carbon neutral operations by 2040.
2021
FedEx Dataworks introduced its first solution, FedEx Surround, a digital platform designed to help digitize our customers' supply chains with breakthrough, real-time inventory tracking and logistics management, which was instrumental in distributing the COVID-19 vaccine.
2022
FedEx Dataworks is designated as its own operating company with the mission of making supply chains smarter for everyone to transform the supply chain from “just-in-time” to “peace-of-mind.”
2023
On April 17, 2023, FedEx celebrates 50 years of driving what's next.
Expanding our footprint
Here are some acquisitions that have helped us extend our reach.
1984
Gelco Express International
1989
Tiger International
1995
Evergreen International Airlines






1998
Caliber System and its subsidiaries: RPS, Roberts Express, Viking Freight, Caribbean Transportation Services, Caliber Logistics, and Caliber Technology
2000–2001
Acquisitions rebranded as part of the FedEx family, including FedEx Express, FedEx Ground, FedEx Custom Critical, FedEx Global Logistics, and FedEx Freight; FedEx Corporate Service, Inc. (or “FedEx Services”) formed to centralize sales, marketing, customer service, and IT support for FedEx Express and FedEx Ground
2000
Tower Group International, rebranded as FedEx Trade Networks and then FedEx Logistics
2001
American Freightways
2004
Kinko’s, rebranded as FedEx Kinko’s, then as FedEx Office in 2008
2004
Parcel Direct, rebranded as FedEx Ground® Economy
2006
ANC Holdings (U.K.), rebranded as FedEx UK; Watkins Motor Lines
2007
Tianjin Datian W. Group (China)—50% share of the joint venture between FedEx and DTW International Priority Express, along with DTW Group’s domestic express network in China
2007
Flying-Cargo (Hungary)
2011
Prakash Air Freight (PAFEX) and AFL/Unifreight India
2011
MultiPack (Mexico)
2012
Opek (Poland)
2012
TATEX (France)
2012
Rapidão Cometa (Brazil)
2014
Supaswift businesses (South Africa, Botswana, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Swaziland, and Zambia)
2014
Bongo International, rebranded as FedEx Cross Border (North America)
2015
GENCO, rebranded as FedEx Supply Chain (North America)
2016
TNT Express (Europe)
2017
Northwest Research
2018
P2P Mailing Limited